Prediabetes: Symptoms, Risks, and Prevention
Prediabetes is a relatively new term in the medical world, but it’s quickly becoming a major health concern worldwide. It’s estimated that about 84 million adults in the United States alone have prediabetes, which can lead to type 2 diabetes if left untreated. Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Understanding the symptoms, risks, and prevention methods of prediabetes is essential to maintaining good health.
In this post, we’ll give you an overview of what prediabetes is, how it develops, and how you can prevent it from progressing into type 2 diabetes. We’ll cover everything from lifestyle changes to medications and other treatments that can help you manage your prediabetes and lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
What is Prediabetes?
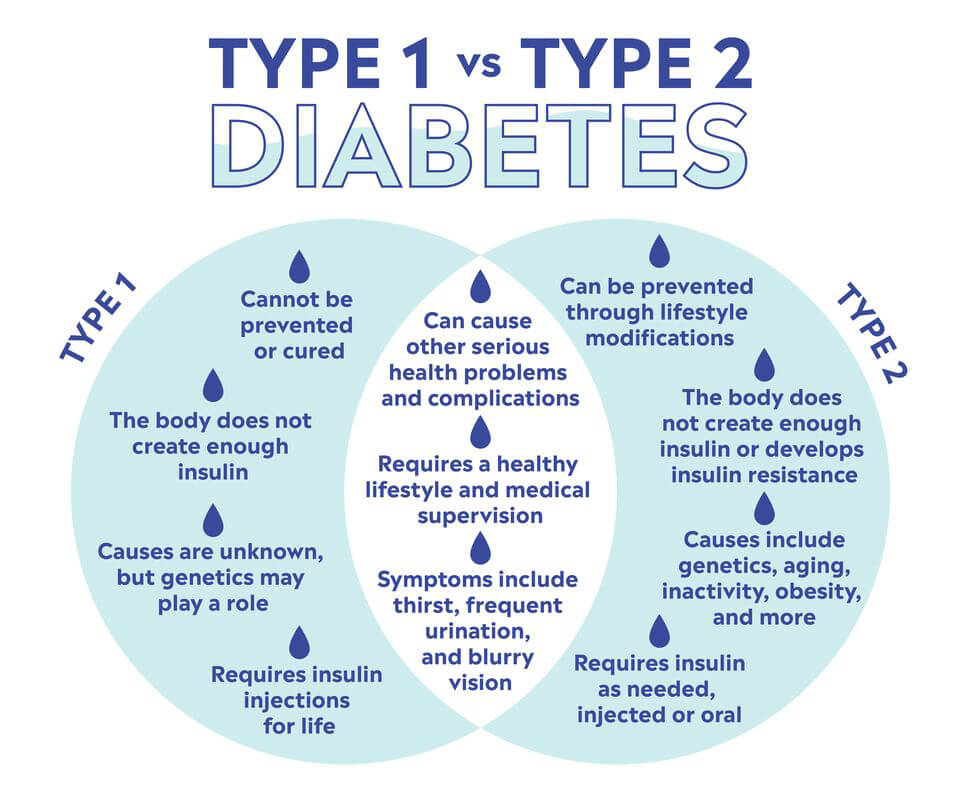
Prediabetes is a condition characterized by higher than normal blood sugar levels, but not yet reaching the threshold for a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. It serves as a warning sign that the body is not effectively using insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Individuals with prediabetes often exhibit symptoms similar to those of diabetes, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. However, these symptoms may be mild or go unnoticed, making prediabetes a silent epidemic that often goes undiagnosed.
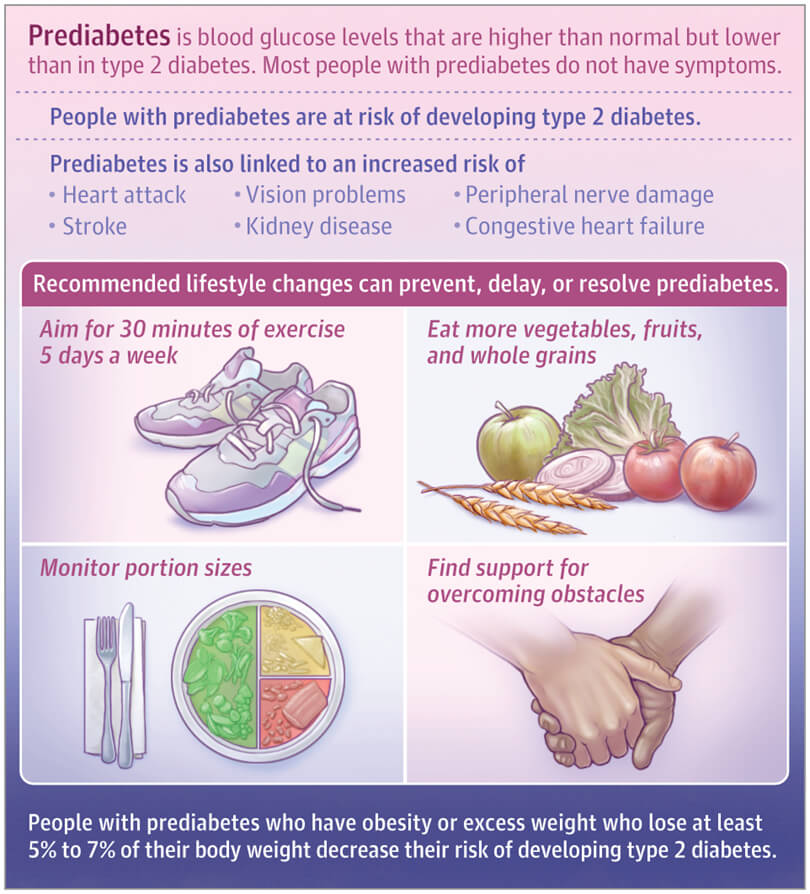
The risks associated with prediabetes are significant. If left unaddressed, it can progress into type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition that requires lifelong management. Furthermore, prediabetes increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes.
However, the good news is that prediabetes is reversible and can often be prevented from progressing into diabetes with timely intervention.
Symptoms of Prediabetes
Prediabetes often presents no clear symptoms. However, a possible indication is darkened skin in certain areas like the neck, armpits, and groin. As prediabetes progresses to type 2 diabetes, symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, heightened hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, numbness or tingling in extremities, frequent infections, slow-healing sores, and unintended weight loss.
While prediabetes often does not exhibit noticeable symptoms, there are certain signs that individuals should be aware of. These symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds, and recurrent infections. It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be attributed to other health conditions, which is why it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.

Early detection of prediabetes is crucial as it provides an opportunity for proactive lifestyle changes to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels through routine medical check-ups, particularly for individuals with risk factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, and unhealthy eating habits, is essential.
Prediabetes Risks and Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of prediabetes. One of the primary risk factors is excess weight, especially around the abdomen. This excess weight causes insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin.
The exact cause of prediabetes is unknown, but family history and genetics play a significant role. It stems from the body’s impaired ability to process sugar (glucose) properly. Risk factors include:
- being overweight
- having a large waist size
- an unhealthy diet
- physical inactivity
- age (increased risk after 35)
- family history
- certain ethnicities (Black, Hispanic, American Indian, and Asian American)
- history of gestational diabetes
- polycystic ovary syndrome
- obstructive sleep apnea
- smoking.
Conditions like high blood pressure, low levels of HDL cholesterol, and high triglycerides also elevate the risk
Early Detection and Diagnosis
One of the challenges of prediabetes is that it often goes unnoticed, as it may not present any noticeable symptoms. However, certain signs can indicate the presence of this condition. These include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention and get tested for prediabetes.
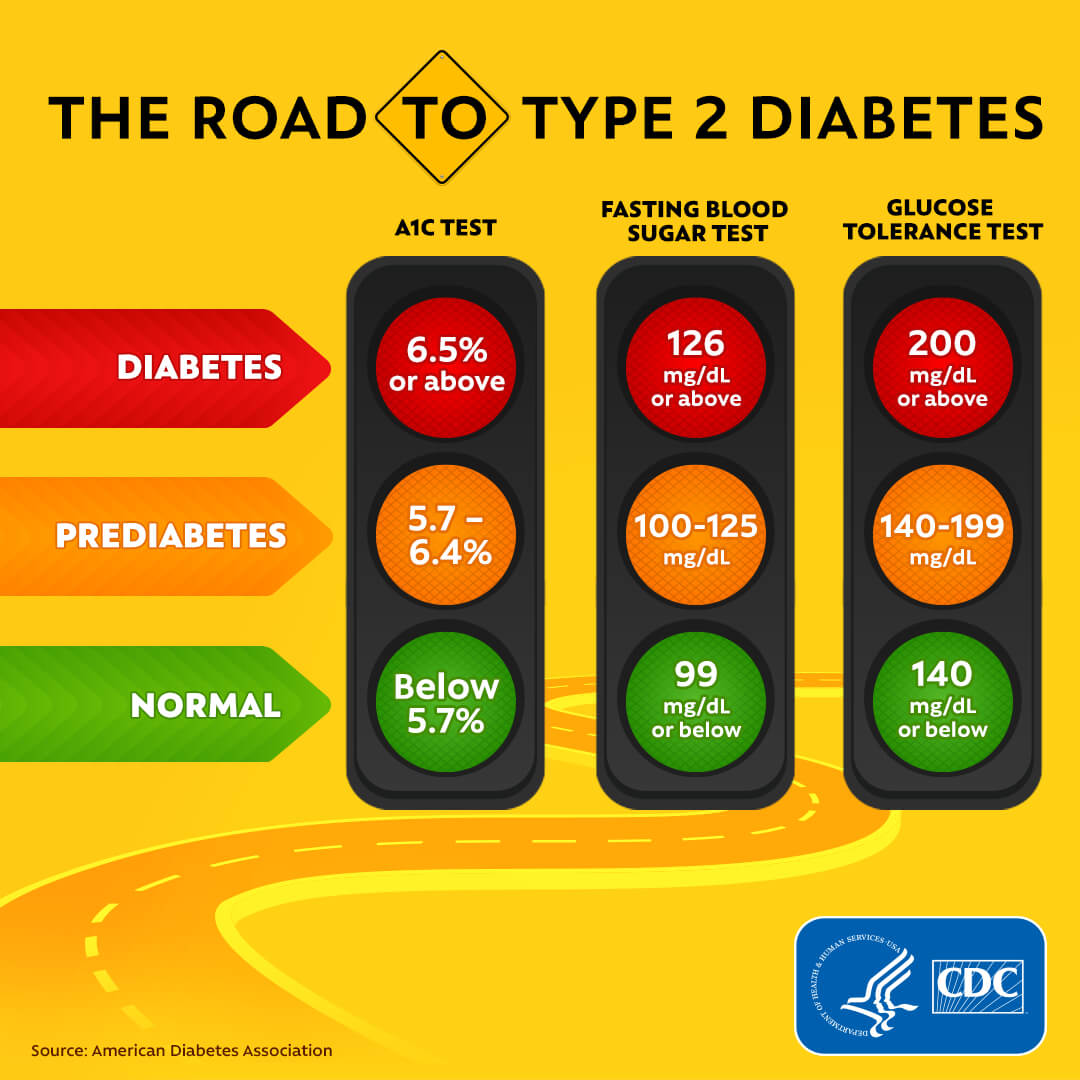
The American Diabetes Association recommends diabetes screening for adults beginning at age 35, or earlier if overweight with additional risk factors. Gestational diabetes history warrants regular checks. Diagnosis involves several blood tests, including the Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test, fasting blood sugar test, and oral glucose tolerance test. These tests measure average blood sugar levels over months, fasting blood sugar levels, and blood sugar response to a sugary liquid, respectively
The significance of early detection lies in the fact that prediabetes is reversible with appropriate lifestyle changes. Making modifications in diet, incorporating regular exercise, and managing stress levels can help improve insulin sensitivity and prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. However, without timely detection, the window of opportunity to make these changes may be missed, leading to the progression of prediabetes into full-blown diabetes.
Early diagnosis allows healthcare professionals to provide tailored guidance and support to individuals with prediabetes. They can create personalized treatment plans, educate patients about the risks associated with the condition, and monitor their progress closely.
How Prediabetes can progress to Type 2 Diabetes
When someone has prediabetes, their blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. However, if left unmanaged, prediabetes can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes over time.
Prediabetes can cause long-term damage to the heart, blood vessels, and kidneys, even without progressing to type 2 diabetes. It is also linked to silent heart attacks. If it progresses to type 2 diabetes, risks include:
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- heart disease
- stroke
- kidney disease
- nerve damage
- fatty liver disease
- eye damage
- and possible amputations.
Fortunately, the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed through lifestyle modifications. Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are all effective strategies. Additionally, managing stress levels, getting enough sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption can also play a significant role in preventing the development of type 2 diabetes.
Prevention strategies for prediabetes
While prediabetes is a serious condition, the good news is that it can often be reversed with lifestyle changes. Here are some effective prevention strategies to consider:
1. Adopt a healthy eating plan
Focus on a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Minimize the consumption of sugary foods and beverages, processed foods, and saturated fats. Opt for complex carbohydrates and fiber-rich foods to help regulate blood sugar levels.

2. Engage in regular physical activity
Incorporate regular exercise into your daily routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Additionally, include strength training exercises to build muscle mass and improve insulin sensitivity.
3. Maintain a healthy weight
Losing excess weight and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in preventing prediabetes. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can make a significant difference in reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Focus on a combination of healthy eating and regular physical activity to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
4. Limit sedentary behavior
Prolonged sitting or a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of prediabetes. Take breaks from sitting every hour and incorporate more movement into your day. Stand while working, take regular walks, and find opportunities to be active throughout the day.
5. Reduce stress levels
Chronic stress can impact blood sugar levels and increase the risk of prediabetes. Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in relaxation exercises, getting enough sleep, and finding healthy outlets for stress, such as hobbies or socializing.
6. Get regular check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring your overall health, including your blood sugar levels. Work closely with your healthcare provider to assess your risk factors, receive appropriate screenings, and discuss any necessary interventions or lifestyle modifications.
Nutrition and Exercise
it is important to focus on a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients and fiber while keeping blood sugar levels stable. Avoiding processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates is crucial in managing blood sugar levels and preventing insulin resistance.

Physical activity is equally important in preventing prediabetes. Regular exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels. Engaging in activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or even dancing for at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week, can have a significant impact on preventing prediabetes.
Incorporating strength training exercises into your routine is also beneficial as it helps build muscle mass, which aids in better glucose control. Additionally, staying physically active throughout the day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or walking instead of driving short distances, can contribute to overall increased physical activity levels.
Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to create a personalized plan that suits your individual needs and goals. They can provide guidance on portion control, meal planning, and exercise routines tailored to your specific situation.
Seeking medical advice and support
If you suspect you may have prediabetes or have been diagnosed with prediabetes, seeking medical advice and support is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Prediabetes is a serious health concern that can progress to type 2 diabetes if left untreated or unmanaged.

A healthcare professional, such as your primary care physician or endocrinologist, can provide expert guidance on developing a personalized management plan tailored to your specific needs and health goals. They will conduct a thorough assessment, which may include reviewing your medical history, conducting physical examinations, and ordering lab tests to determine your blood sugar levels and assess your overall health.
With their expertise, they can help you understand the symptoms and risks associated with prediabetes, such as elevated blood sugar levels, increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. They can also help you identify potential risk factors, such as family history, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and unhealthy eating habits, which contribute to the development of prediabetes.
Remember, seeking medical advice and support is not only important for managing prediabetes but also for preventing its progression to type 2 diabetes. Your healthcare team will serve as your trusted partners in your journey towards better health, providing the knowledge, resources, and support you need to take control of your prediabetes and reduce your risk of developing diabetes and its complications.
Conclusion
We hope you found our blog post on the prediabetes epidemic informative and insightful. Prediabetes is a growing health concern, and understanding its symptoms, risks, and prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining good health.
By recognizing the warning signs and implementing lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Remember, knowledge is power, and by taking action now, you can take control of your health and prevent the progression of prediabetes. Stay informed, stay proactive, and stay healthy!